Theory Application
Theory Application
Theory Application
Work in fluid systems occurs due to pressure differentials, such as those exerted by air or water in a syringe. This pressure difference, represented by P-Pₒ, dictates the direction and magnitude of the work done. By integrating this pressure difference over a change in volume (dV), the total work input for a process can be calculated. This integration accounts for variations in pressure and volume, providing a comprehensive measure of the work done by or on the fluid during the process.
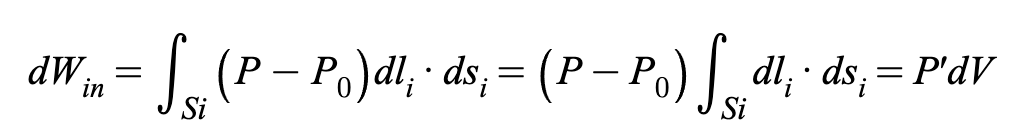 (1)
(1)
For equation 1, P is the absolute internal gas pressure, P0, the environment pressure (1 atm = 1.0336 bar),
P', the relative pressure, Si, the total inner surface, dsi the area vector, dli, the inner surface
displacement, and dV, the volume change. [1]
Citations
[1] C. - P. Chou and B. Hannaford, “Measurement and modeling of McKibben pneumatic artificial muscles,” Robotics and Automation, IEEE Transactions on, vol. 12, no. 1, pp. 90-102, 1996.